Iot Integration Manufacturing Guide
Manish Kumawat
Last Updated on: 07 October 2025
What an exciting experience if your fridge texts you to tell you you're out of milk, or you wake up and your coffee machine begins to prepare a cup of coffee. You could have smart light bulbs that you can dim or turn on from your phone, no matter where you are. Or, maybe you have a fitness tracker that monitors your heart rate and sends that info to your phone so you can see how your workout is going. That's kind of the idea behind the Internet of Things (IoT), but for everything, not just your kitchen. It's like turning everyday objects into superheroes with superpowers – the superpower of being connected to the internet.
But it's not all about gadgets and personal use. Cities can use connected traffic lights to keep things moving smoothly. Farmers can even use sensors in their fields to monitor soil moisture and their watering. Businesses are using IoT in a big way too. Factories can have machines that track their own performance and send alerts if something's about to go wrong.
Here's the basic idea: Lots of things around us, from cars to thermostats, are getting embedded with tiny computers, sensors, and transmitters. These connections allow them to collect data (like the temperature in your room) and then send that data over the internet (like sending a text message). This lets them work together and even be controlled remotely using your phone or computer.
Components of IoT (Internet of Things)
- Devices/Sensors: Collect data from the environment (e.g., temperature sensors, GPS, cameras).
- Connectivity: Methods to transmit data (e.g., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular, Zigbee).
- Data Processing: Processing and analyzing the gathered data, frequently via edge devices or cloud servers.
- User Interface: Interface for users to interact with the IoT system (e.g., mobile apps, web dashboards).
- Network: Infrastructure enabling communication between devices and central systems (e.g., routers, gateways).
- Actuators: Devices that take action based on data processed (e.g., motors, lights, valves).
- Security: Protocols and measures to ensure data integrity, confidentiality, and availability (e.g., encryption).
- Data Storage: Systems to store the vast amount of data generated (e.g., databases, cloud storage).
- Protocols: Communication protocols to enable device interaction (e.g., MQTT, CoAP, HTTP).
- Analytics: Methods and instruments to extract knowledge and trends from the gathered information.
- Cloud Computing: Remote data processing, storage, and management servers.
- Edge Computing: Data processing closer to the source to cut down on latency and bandwidth consumption.
- Power Management: Systems to ensure devices are powered effectively and efficiently (e.g., batteries, energy harvesting).
Key Aspects of IoT Integration in Manufacturing Websites
Live Monitoring and Analytics
- Live Dashboards: Display real-time data from IoT devices on the production floor. Machine status, production metrics, and environmental conditions may be included in this.
- Analytics and Insights: Offer data analysis tools that help in identifying trends, optimizing processes, and predicting maintenance needs.
Remote Management and Control
- Device Control: Allow authorized personnel to control machinery and equipment remotely through the website.
- Alerts and Notifications: Set up systems to send alerts or notifications via the website when certain conditions are met, such as machine malfunctions or production anomalies.
Predictive Maintenance
- Condition Monitoring: Use IoT sensors to continuously monitor the condition of equipment and predict when maintenance is needed, reducing downtime.
- Maintenance Scheduling: Integrate with maintenance management systems to schedule and track maintenance activities.
Supply Chain Optimization
- Inventory Management: Monitor inventory levels in real time and automate reordering processes based on usage data.
- Logistics Tracking: Track the location and status of shipments, providing visibility into the supply chain.
Quality Control
- Product Tracking: Track the production process of each item.
- Defect Detection: Use IoT-enabled sensors to detect defects.
Energy Management
- Energy Consumption Monitoring: Monitor energy usage across the facility to identify areas for improvement and cost savings.
- Automation for Efficiency: Implement automated systems to control lighting, heating, and cooling based on real-time data.
Steps for Integrating IoT into a Manufacturing Website
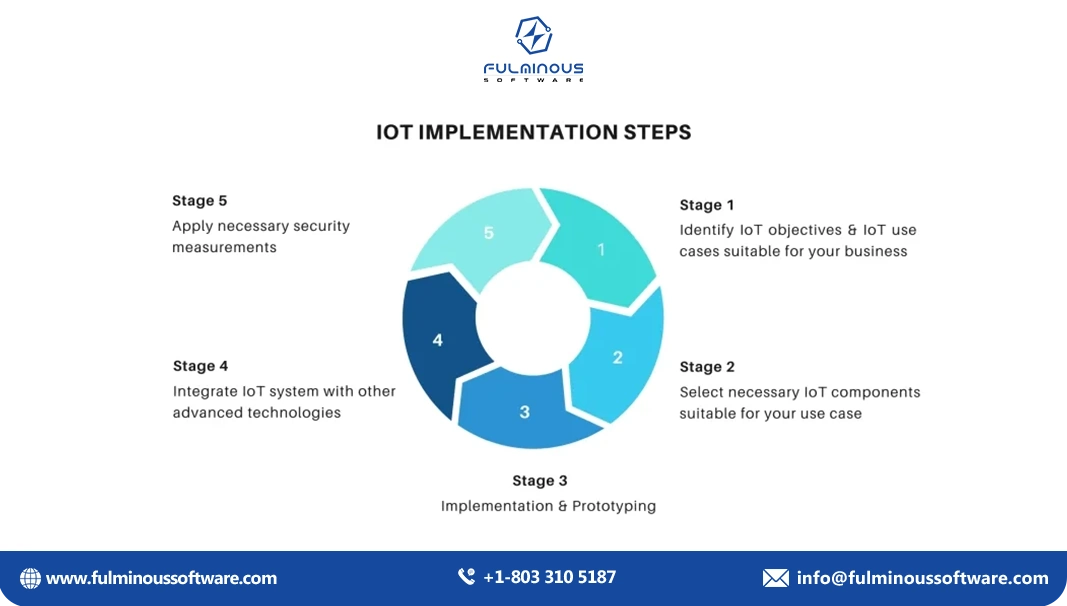
- Define Objectives and Use Cases: Identify the key goals for IoT integration (e.g., improving efficiency, reducing downtime, enhancing quality control). Determine specific use cases and the type of data needed.
- Choose the Right IoT Platform: Select an IoT platform that is compatible with your existing systems and can handle the scale of your operations. Ensure necessary features such as data analytics, real-time monitoring, and device management.
- Deploy IoT Devices and Sensors: Install IoT devices and sensors on equipment and production lines. Ensure proper connectivity and data transmission capabilities.
- Develop the Website Interface: Design a user-friendly interface that displays IoT data in an intuitive manner. Incorporate features like dashboards, reports, and control panels.
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Ensure integration with existing ERP, CRM, and management systems. Use APIs and middleware.
- Implement Security Measures: Protect IoT devices and data from possible cyber threats. Regularly update and patch devices and software to address vulnerabilities.
- Train Staff and Monitor Performance: Train employees on how to use the IoT-enabled website and tools. Monitor the performance of the system continuously and make improvements as needed.
The Influence of IoT on Manufacturing Business Operations
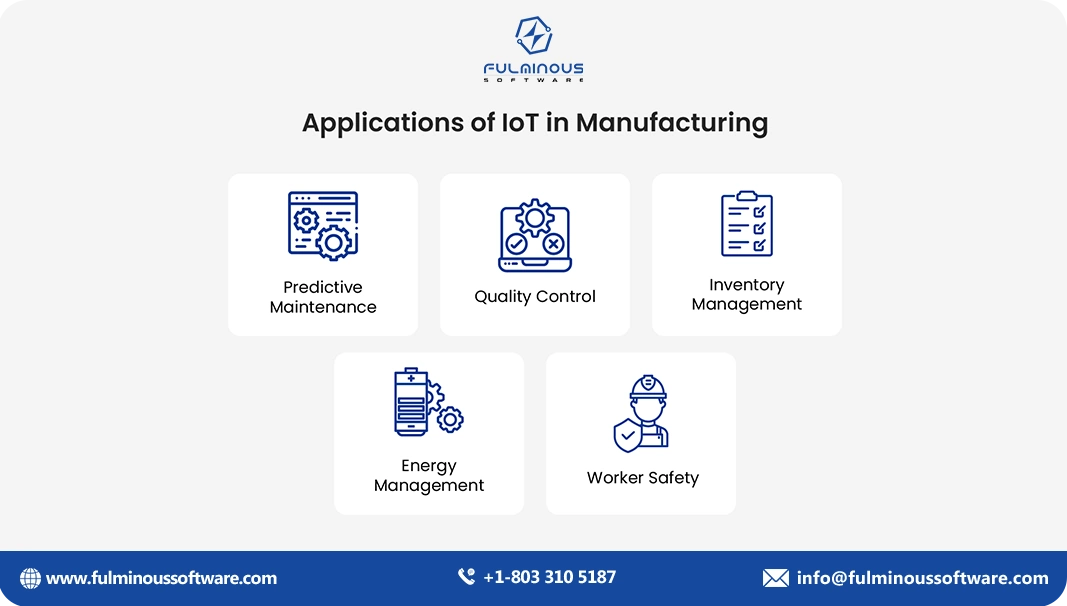
See the role of IoT in Manufacturing business process:
Predictive Maintenance:
Imagine a machine that can tell you when it's about to malfunction before it actually breaks down and throws a break into your production schedule. It's possible to prepare for equipment failures and plan maintenance in advance when you have IoT sensors tracking variables like temperature and vibration. Businesses can avoid unplanned downtime and save money by keeping their manufacturing lines running smoothly.
Boosting Efficiency:
Those tiny sensors we mentioned can track everything from material usage to energy consumption. Manufacturers can find areas for improvement by evaluating this data. Perhaps there's waste in the production process, or perhaps a machine is drawing more energy than it needs to. Factories can maximize resource efficiency, streamline workflows, and optimize operations with the use of this information.
Improved Quality Control:
Say goodbye to relying solely on random inspections to catch defects. With IoT, machines can be equipped with smart sensors that monitor product quality at every stage of the production line. These sensors can detect even the smallest imperfections, ensuring consistent quality and reducing the risk of faulty products reaching customers.
Remote Monitoring and Control:
Imagine being able to monitor your entire factory floor from the comfort of your couch (or even a beach!). With IoT, key performance indicators (KPIs) can be tracked remotely, allowing managers to make adjustments or troubleshoot issues in real time. This remote access also lets them identify opportunities for improvement and optimize production even when they're not physically present on the factory floor.
Enhanced Safety:
Accidents happen, but IoT can help prevent them. Sensors can be used to monitor things like air quality, noise levels, and even worker movement. This data can be used to identify potential safety hazards and implement measures to keep workers safe. For example, a sensor might detect a gas leak and trigger an automatic shut-off valve, preventing a potential disaster.
Happy Customers, Happy Business:
By improving efficiency, quality control, and overall production processes, IoT ultimately leads to happier customers. Consistent product quality, timely deliveries, and potentially even lower costs – all these factors contribute to a better customer experience. After all, happy customers are more likely to come back for more.
Challenges of IoT Integration in Manufacturing Websites
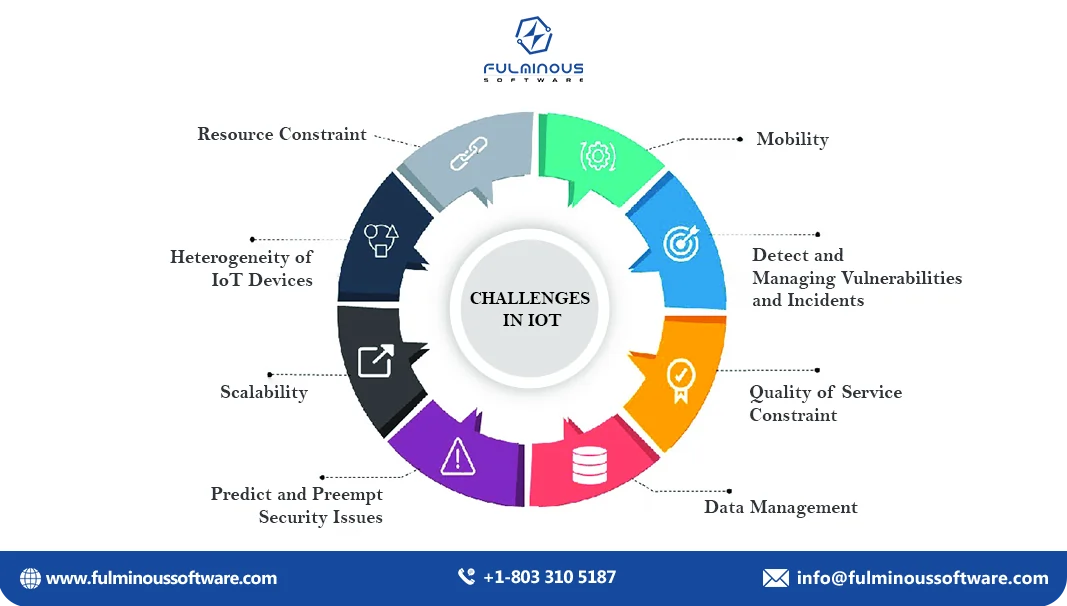
The Internet of Things (IoT) stands for a world of connected machines, live data, and optimized production. While the benefits are undeniable, navigating the challenges of IoT integration requires careful planning.
Security Nightmares
Imagine a hacker taking control of your assembly line through a rogue sensor. With so many devices talking to each other and your website, a single breach can wreak havoc.
- Multiple Entry Points: Every sensor, device, and communication channel becomes a potential vulnerability. Hackers only need to find one weak link to disrupt your entire operation.
- Legacy Systems: Integrating older, less secure equipment with newer IoT devices can create security gaps.
- Data Deluge: The sheer volume of data collected by IoT sensors creates a treasure trove for hackers.
Data Digestion Dilemma
Data is the lifeblood of IoT, but drowning in an ocean of information isn't helpful. Here's the problem:
- Making Sense of the Mess: Extracting meaningful insights from the mountains of data requires robust analytics tools and skilled personnel.
- Storage Blues: Storing all that data securely can be expensive.
- Information Overload: Describing the right data in a clear, concise way on your website is paramount.
Integration Intrigue
Imagine a symphony where the instruments refuse to play together. That's what a poorly integrated IoT system feels like.
- Legacy Blues: Connecting old, non-IoT equipment with newer devices can be tricky.
- Standardization Struggles: The lack of universal standards in IoT can cause compatibility issues. Mixing and matching devices from different vendors might lead to integration headaches.
- Data Silos: Data collected by various systems might not communicate with each other, creating isolated pockets of information.
Cost Considerations
Upgrading your website with IoT isn't exactly pocket change.
- Initial Investment: Sensors, software, data storage, and website development all come at a cost.
- Ongoing Expenses: Maintaining the system, updating software, and managing data security are ongoing costs that need to be factored in.
- Hidden Costs: Integration challenges, security vulnerabilities, and data management issues can lead to unforeseen expenses.
Skilled Staff Scarcity
Not everyone can speak the language of IoT.
- Technical Expertise: You'll need personnel who understand IoT, data analysis, and website development.
- Change Management: Implementing IoT requires a change in mindset and workflows for your employees.
- Data Literacy: Employees need to understand how to interpret and utilize the data generated by IoT systems for effective decision-making.
Overcome The Challenges: Strategies for Successful IoT Integration in Manufacturing
Despite the challenges, the potential of IoT in manufacturing is undeniable. Here are some tips to navigate the roadblocks:
- Start Small, Scale Smart: Don't try to overhaul your entire website at once. Begin with a pilot project.
- Prioritize Security: Implement robust security measures from the get-go. Regularly update software, patch vulnerabilities, and encrypt data transmission.
- Invest in Analytics: Choose tools that can analyze and visualize data effectively. Focus on extracting actionable insights.
- Embrace Open Standards: Opt for devices and platforms that comply with open standards for easier integration.
- Plan for Scalability: Design your website and data infrastructure with future growth in mind.
- Develop a Skilled Workforce: Invest in training your existing staff or hire personnel with expertise in IoT, data analysis, and website development.
Conclusion
So, there you have it! The Internet of Things (IoT) is like giving your factory superpowers. Imagine machines that practically run themselves, catching problems before they happen, and keeping things humming along smoothly. With IoT, you can see what's going on from anywhere (even the beach!), waste less energy and materials, and make sure your customers get top-notch products every time. Of course, there are some hurdles to overcome. But the payoff is huge – a smarter, more efficient factory that keeps you ahead of the curve. In short, IoT is the ultimate workshop upgrade for manufacturers.
FAQs
- Q1: What is IoT in manufacturing?
- A: IoT in manufacturing involves using internet-connected devices and sensors to collect and analyze data, improving efficiency, maintenance, and quality control.
- Q2: How does IoT improve predictive maintenance?
- A: IoT enables predictive maintenance by using sensors to monitor equipment conditions, predict failures, and schedule maintenance before issues cause downtime.
- Q3: What are the key components of IoT?
- A: Key components include sensors (data collection), computers (data processing), transmitters (data transmission), connectivity (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth), data platforms (storage), user interfaces, and security measures.
- Q4: What are the benefits of IoT integration?
- A: Benefits include improved operational efficiency, enhanced decision-making, cost savings, increased uptime, and better quality control through real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Q5: How do you ensure IoT security?
- A: Ensure IoT security by implementing robust protocols, encrypting data, regularly updating software, patching vulnerabilities, and using secure networks to protect against cyber threats.
- Q6: What are common challenges in IoT integration?
- A: Challenges include security risks, data management, integration with legacy systems, high initial costs, and the need for skilled staff for implementation and maintenance.
HIRE A TOP SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT COMPANY

 Verified
Expert in Software & Web App Engineering
Verified
Expert in Software & Web App Engineering
I am Manish Kumawat, co-founder of Fulminous Software, a top leading customized software design and development company with a global presence in the USA, Australia, UK, and Europe. Over the last 10+ years, I am designing and developing web applications, e-commerce online stores, and software solutions custom tailored according to business industries needs. Being an experienced entrepreneur and research professional my main vision is to enlighten business owners, and worldwide audiences to provide in-depth IT sector knowledge with latest IT trends to grow businesses online.
Partner with Top-Notch Web Application Development Company!
Discuss your Custom Application Requirements on info@fulminoussoftware.com or call us on +1-903 488 7170.
15 Days Risk-Free TrialRecommended Articles


